Enhanced Collagen Support
Support your body's collagen production and maintenance through gut microbiome optimization for firmer, more youthful-looking skin.
Key Supporting Microbes
These beneficial microorganisms play key roles in supporting this health benefit:
Collagen: The Foundation of Youthful Skin
Collagen is the most abundant protein in your body, making up about 75% of your skin's dry weight. It provides the structural framework that keeps skin firm, plump, and resilient. As collagen production naturally declines with age—approximately 1% per year after age 20—skin loses its youthful appearance.
What's increasingly understood is that collagen health isn't just about what you put on your skin or even what you eat—your gut microbiome plays a significant role in collagen metabolism, absorption of collagen-supporting nutrients, and the inflammatory processes that accelerate collagen breakdown.[1]
How the Gut Affects Collagen
Nutrient Absorption for Collagen Synthesis
Collagen production requires specific nutrients, all absorbed through the gut:
Vitamin C:
- Absolutely essential for collagen synthesis
- Serves as a cofactor for enzymes that stabilize collagen
- Deficiency causes collagen to be unstable
- Gut health affects vitamin C absorption
Amino acids:
- Glycine, proline, and hydroxyproline are collagen building blocks
- Protein digestion and absorption depend on gut function
- Hypochlorhydria (low stomach acid) impairs protein breakdown
- Gut inflammation can reduce amino acid absorption
Zinc:
- Required for collagen synthesis enzymes
- Gut bacteria affect zinc bioavailability
- Common deficiency in those with gut issues
- Essential for wound healing
Copper:
- Needed for cross-linking collagen fibers
- Cross-linking provides structural strength
- Gut health affects copper absorption
Inflammation and Collagen Degradation
Chronic inflammation accelerates collagen breakdown:
- Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) digest collagen
- Inflammation upregulates MMP activity
- Gut-derived inflammation reaches skin via circulation
- Anti-inflammatory bacteria help protect collagen
Collagen Peptide Absorption
When you consume collagen supplements:
- They must be broken down in the gut
- Absorption of peptides depends on gut health
- Some peptides are absorbed intact and signal skin cells
- Gut bacteria may influence this process
The Estrobolome Connection
In women, gut bacteria affect estrogen levels:
- Estrogen stimulates collagen production
- The "estrobolome" (gut bacteria that metabolize estrogen) matters
- Dysbiosis can lead to estrogen imbalances
- This affects skin collagen status, especially around menopause
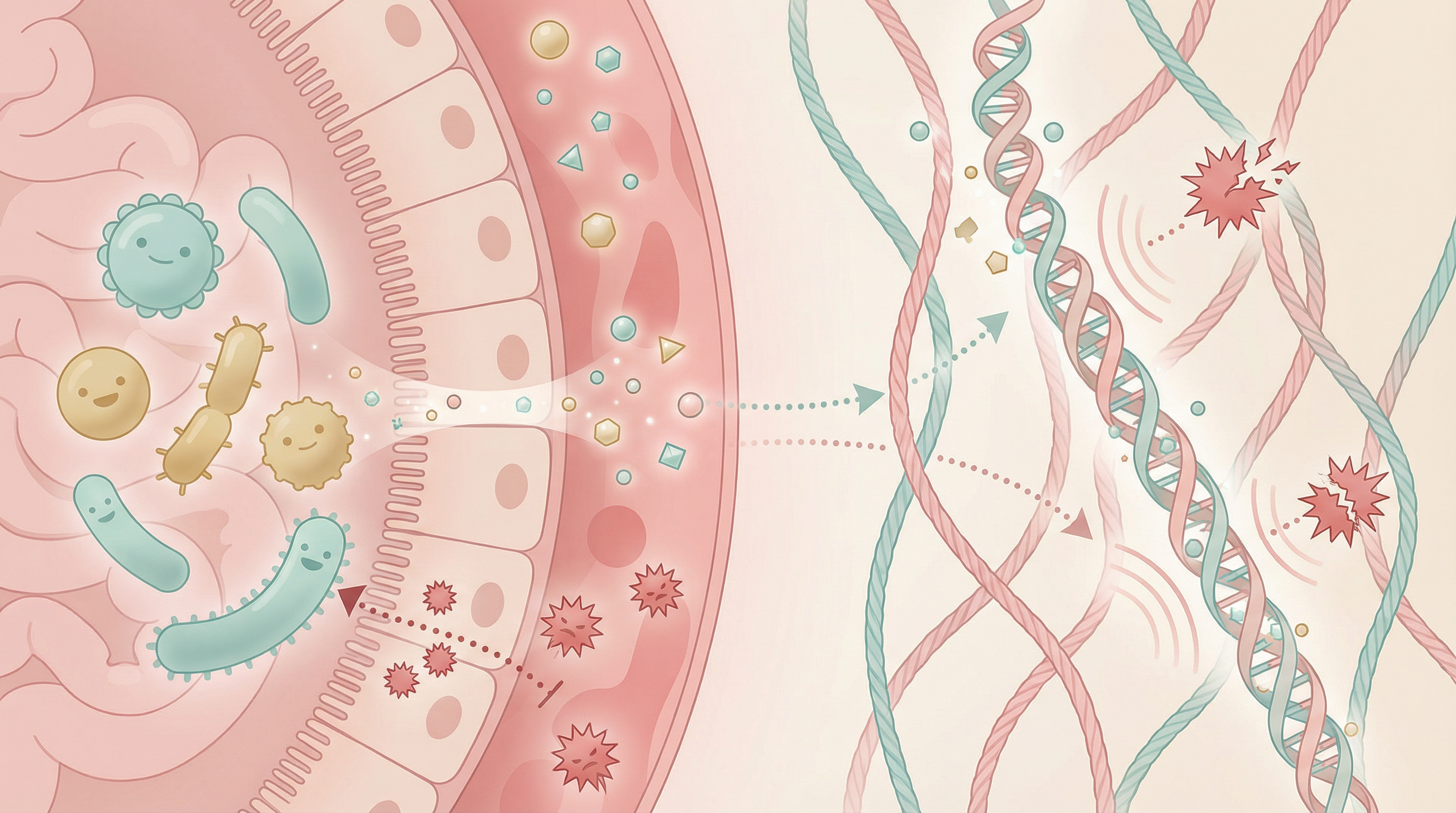
Key Microbes for Collagen Support
Lactobacillus plantarum
Research shows skin benefits:[2]
- When combined with collagen, improves skin elasticity
- Reduces wrinkle depth in studies
- May enhance collagen peptide absorption
- Anti-inflammatory effects protect existing collagen
Bifidobacterium breve
Supports skin from within:[3]
- Improves skin hydration and elasticity
- May support collagen metabolism
- Strain B-3 particularly studied
- Reduces transepidermal water loss
Lactobacillus casei
Contributes to skin health:
- Supports overall gut health
- May improve nutrient absorption
- Anti-inflammatory properties
- Part of effective probiotic combinations
Akkermansia muciniphila
Indirect collagen support:
- Reduces systemic inflammation
- Supports gut barrier function
- Associated with better metabolic health
- May reduce collagen-degrading inflammation
Signs of Collagen Decline
Your skin may need collagen support if you notice:
- Loss of skin firmness and elasticity
- Fine lines and wrinkles increasing
- Skin that doesn't "bounce back" when pinched
- Thinning skin, especially on hands
- Sagging, particularly along jawline
- Slower wound healing
- Cellulite becoming more visible
- Joint stiffness (collagen is also in joints)
Dietary Strategies for Collagen Support
Collagen-Building Foods
Bone broth:
- Natural source of collagen and gelatin
- Contains glycine and proline
- Easy to digest
- Make at home or buy quality prepared
Collagen-rich proteins:
- Skin-on chicken
- Fish with skin
- Organ meats
- Egg whites (contain proline)
Vitamin C-rich foods (essential):
- Citrus fruits
- Bell peppers
- Strawberries and kiwi
- Broccoli and leafy greens
Zinc sources:
- Pumpkin seeds
- Beef and lamb
- Chickpeas
- Cashews
Copper sources:
- Oysters and shellfish
- Nuts and seeds
- Dark chocolate
- Organ meats
Collagen-Protective Foods
Antioxidants protect collagen from oxidative damage:
- Berries (anthocyanins)
- Green tea (EGCG)
- Tomatoes (lycopene)
- Dark leafy greens
Anti-inflammatory foods reduce collagen breakdown:
- Fatty fish (omega-3s)
- Turmeric
- Ginger
- Extra virgin olive oil
Foods That Damage Collagen
Limit these collagen-destroyers:
Sugar:
- Causes glycation, which stiffens and damages collagen
- Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) accumulate
- High-glycemic foods are particularly problematic
Excessive alcohol:
- Dehydrates skin
- Increases inflammation
- Impairs nutrient absorption
- Directly damages collagen
Processed foods:
- Often high in sugar and inflammatory fats
- May contain AGE-promoting compounds
- Displace nutrient-dense foods

Collagen Supplementation
Types of Collagen Supplements
Collagen peptides (hydrolyzed collagen):
- Broken down for easier absorption
- Can stimulate collagen production
- Most common supplement form
- Research supports skin benefits
Gelatin:
- Partially hydrolyzed collagen
- Used in cooking and supplements
- May support gut health too
- Less well-absorbed than peptides
Maximizing Supplement Effectiveness
For best absorption and utilization:
- Take with vitamin C
- Ensure gut health for optimal absorption
- Consistent daily use shows best results
- Look for quality, tested products
- Benefits typically seen at 8-12 weeks
Lifestyle Factors
Sun Protection
UV damage is the primary external collagen destroyer:
- UVA penetrates deeply and damages collagen
- Increases MMP activity
- Use broad-spectrum SPF daily
- Seek shade during peak hours
- Consider protective clothing
Avoid Smoking
Smoking devastates collagen:
- Reduces vitamin C levels dramatically
- Increases free radical damage
- Impairs blood flow to skin
- Accelerates aging significantly
Sleep
Growth hormone release during sleep supports collagen:
- Most collagen synthesis occurs at night
- Sleep deprivation impairs repair processes
- Prioritize 7-9 hours
- Silk pillowcases may reduce mechanical damage
Exercise
Physical activity supports collagen:
- Improves circulation to skin
- May stimulate collagen production
- Supports overall health
- Avoid excessive sun exposure during outdoor exercise
Building Better Collagen Support
Supporting collagen through the gut-skin axis involves:
- Optimizing gut health for nutrient absorption
- Ensuring vitamin C intake daily from food or supplements
- Including collagen-rich or collagen-boosting foods
- Reducing inflammation that accelerates breakdown
- Protecting from UV damage consistently
- Considering collagen peptide supplementation
Most people notice improvements in skin hydration and texture within 8-12 weeks of consistent collagen-supporting practices. Visible improvements in firmness and fine lines typically develop over 3-6 months, with continued benefits over time.
Supporting Practices
Evidence-based strategies to support this benefit:
- Consume collagen-boosting foods like bone broth and citrus
- Include vitamin C-rich foods essential for collagen synthesis
- Protect skin from UV damage which degrades collagen
- Avoid smoking which accelerates collagen breakdown
- Include copper and zinc-rich foods for collagen enzymes
- Consider collagen peptide supplementation
References
- Vollmer DL, West VA, Lephart ED. Enhancing Skin Health: By Oral Administration of Natural Compounds and Minerals with Implications to the Dermal Microbiome. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018;19(10):3059. doi:10.3390/ijms19103059 ↩
- Kim JE, Kim JS, Kim H, et al.. Oral supplementation with collagen and Lactobacillus plantarum on skin characteristics. Food & Function. 2014;5(12):3195-3205. doi:10.1039/c4fo00772g ↩
- Inoue N, Sugihara F, Wang X. Ingestion of bioactive collagen hydrolysates enhance facial skin moisture and elasticity. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 2016;96(12):4077-4081. doi:10.1002/jsfa.7606 ↩