Micrococcus luteus is a gram-positive, spherical bacterium that is a common and beneficial member of the human skin microbiome. This aerobic organism is known for its distinctive yellow pigmentation and is frequently isolated from healthy human skin, particularly in dry areas of the body.
Key Characteristics
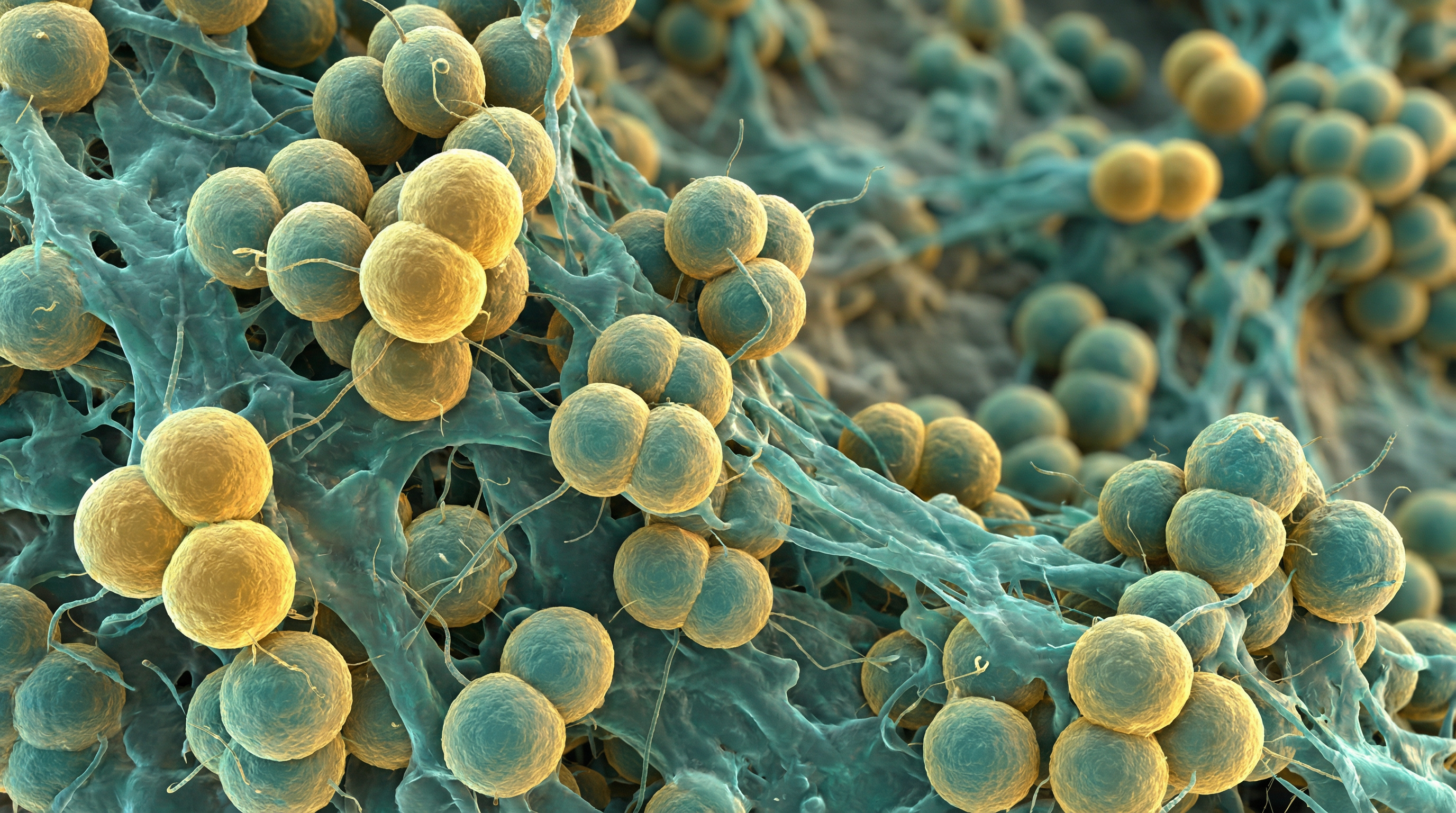
M. luteus is a non-motile, non-spore-forming bacterium that typically grows in tetrads (groups of four cells). It is aerobic, meaning it requires oxygen to grow, which makes it well-adapted to the skin surface environment. The bacterium produces carotenoid pigments that give it its characteristic yellow color, which may provide protection against UV radiation. M. luteus is catalase-positive and can metabolize a variety of carbon sources, allowing it to thrive in the diverse microenvironments of human skin.
Role in Skin Health
Recent research has highlighted several important contributions of M. luteus to skin health:
Skin Hydration: Clinical studies have shown that topical application of M. luteus strains, particularly M. luteus Q24, can significantly improve skin hydration levels. In one study, participants showed a 101% increase in skin hydration after 25 days of probiotic serum application.
Skin Barrier Function: M. luteus influences epidermal thickness and structure, contributing to proper skin barrier function. Research using 3D skin tissue models has demonstrated that M. luteus can reduce epidermal thickness, which may help maintain normal skin turnover and prevent hyperkeratosis.
Cosmetic Benefits: Beyond its physiological effects, M. luteus has been shown to improve cosmetic skin parameters, including reduction in pores, spots, wrinkles, and impurities. These benefits make it a promising candidate for inclusion in skincare formulations.
Microbiome Balance: As a commensal organism, M. luteus contributes to the overall diversity and stability of the skin microbiome. A balanced microbiome is associated with healthy skin and resistance to colonization by potentially harmful microorganisms.
Interaction with Other Microorganisms
M. luteus exists within a complex ecosystem on human skin, interacting with various other microorganisms:
It can coexist with other beneficial skin bacteria like Staphylococcus epidermidis, potentially forming synergistic relationships that enhance skin health.
Studies suggest that M. luteus may help regulate the growth of Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes), the bacterium associated with acne development, contributing to a balanced microbiome.
When part of a mixed microbial community, M. luteus demonstrates more pronounced effects on skin processes than when present alone, highlighting the importance of microbial diversity and community interactions in skin health.
Potential Therapeutic Applications
The beneficial properties of M. luteus have led to growing interest in its use as a probiotic in skincare:
Topical Probiotics: Live M. luteus strains, such as M. luteus Q24 (BLIS Q24™), are being incorporated into serums and other skincare products to improve skin hydration, texture, and appearance.
Skin Disorders: While research is still emerging, the ability of M. luteus to influence skin barrier function and microbiome balance suggests potential applications in managing skin conditions characterized by barrier dysfunction or microbial dysbiosis.
Postbiotics: Beyond live bacteria, there is interest in utilizing postbiotics derived from M. luteus—beneficial compounds produced by the bacterium that may provide skin benefits without requiring live organisms.
Geographic and Demographic Distribution
M. luteus is found on the skin of people across different geographical regions, though its prevalence may vary. Interestingly, some studies have noted differences in M. luteus abundance between populations. For example, research comparing skin microbiome profiles between Cameroonian and Japanese individuals found that Micrococcus was predominantly present in Cameroonian skin samples but mostly absent in Japanese skin samples, suggesting potential influences of genetics, environment, or lifestyle on M. luteus colonization.
Safety Profile
M. luteus is generally recognized as safe for topical application. Clinical studies evaluating the safety and tolerability of topical formulations containing live M. luteus have reported no significant adverse effects, making it a promising candidate for widespread use in skincare products.